openshift
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Workflow comparisson Virtual vs. PAAS
Physical
| Virtual
| PAAS
|
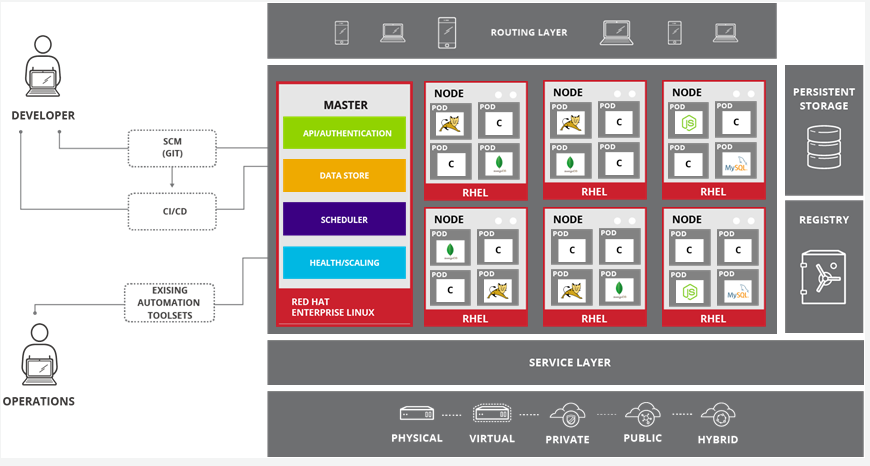
OpenSHift Architecture
- Only x86 platforms supported
- OpenShift runs on either RHEL or Red Hat Enterprise Atomic Host
- Nodes are instances of RHEL 7 or Red Hat Atomic Host with OpenShift installed
- Nodes are orchestrated by masters
- Hybrid approach supports deploying OpenShift instances across all of these infrastructures
- OpenShift is supported anywhere that Red Hat Enterprise Linux is
| Scheduler | Determines placement of new pods onto nodes within OpenShift cluster. Select best-fit node
|
OpenSHift UX
OpenShift CICD
API
# list pods oc get pod
openshift.1519203610.txt.gz · Last modified: (external edit)