Table of Contents
Workflow comparisson Virtual vs. PAAS
Physical
| Virtual
| PAAS
|
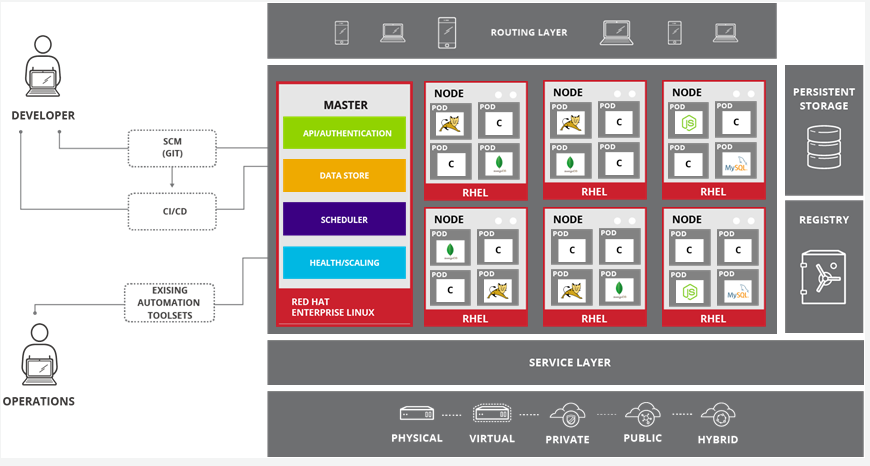
OpenSHift Architecture
- Only x86 platforms supported
- OpenShift runs on either RHEL or Red Hat Enterprise Atomic Host
- Nodes are instances of RHEL 7 or Red Hat Atomic Host with OpenShift installed
- Nodes are orchestrated by masters
- Hybrid approach supports deploying OpenShift instances across all of these infrastructures
- OpenShift is supported anywhere that Red Hat Enterprise Linux is
| Scheduler | Determines placement of new pods onto nodes within OpenShift cluster. Select best-fit node
|
| Replication Controller | Ensures that specified number of pod replicas running at all times. Adds or deletes pods according to life signs. |
| OpenShift Networking |
Scenario: External client points browser to myApp.cloudapps.ml.opentlc.com:80
Scenario: Pod transmits packet to pod in another node host in OpenShift environment
|
| Route | Exposes service by giving it externally reachable hostname (FQDN). |
| Router |
|
| Services |
|
| XXX |
Container Deployment Workflow
Scenario: New application requested via CLI, web console, or API
OpenShift API/authentication layer:
- Approves request, considering user’s permissions, resource quotas, and other information
- Creates supporting resources: deployment configuration, replication controllers, services, routes, and persistent storage claims
OpenShift scheduling layer:
- Designates node host for each pod, considering resources' availability and load and application spread between nodes for application high availability
OpenShift node:
- Pulls down image to be used from external or integrated registry
- Starts container (pod) on node
OpenShift CICD
Update Rollout strategies
| Rolling Update | Pre life cycle hook. Scale up/down new/old pods one by one. Wait for readiness checks. Post life cycle hooks. No downtime. |
| Recreate | Scale down all old. Scale up all new. Has downtime. |
Concepts
| BuildConfig | Definition of the entire build process as code. |
| Build Strategies | Build strategies for building artifacts. Artifact resulting from build depends on builder used to create it.
For Docker and S2I builds, resulting objects are runnable images. For custom builds, resulting object are whatever builder image author specified. |
| Source-to-Image (S2I) Build |
Reproducability. S2I supports incremental builds, which reuse previously downloaded dependencies, previously built artifacts, etc. Security. Builds and runs are executed as root, which may be exposed. S2I can execute commands with less rights. |
| Image Stream |
Docker images from different sources, identified by the same tag. |
| Jenkins pipeline |
During the build the following will then happen
Build via OpenShift pipelines:
More: https://developers.redhat.com/blog/2017/01/09/using-pipelines-in-openshift-3-3-for-cicd/ |
| XXX | |
| XXX | |
| XXX | |
| XXX |
API
# list pods oc get pod